Language data for Guinea
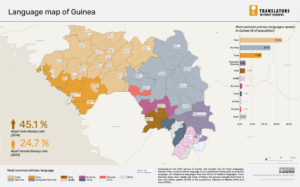
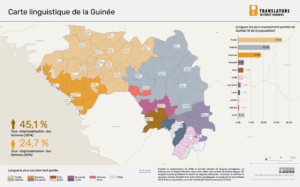
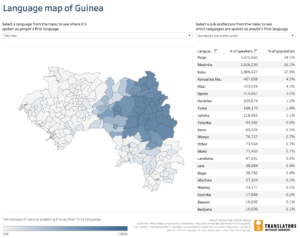
According to the 2014 census of Guinea, the country has 22 major languages. French is the country’s official language, but is used almost exclusively as a second language. Six indigenous languages have the status of national languages: Pular (or Fula), Maninka, Susu, Kissi, Kpelle and Toma. According to the census (see chart below), Pular is the most widely spoken (35% of the population), followed by Maninka (25%) and Susu (18%).
The three languages with the most users are geographically concentrated. Pular is mostly spoken in Middle Guinea (northwestern portion of the country), Maninka in Upper Guinea (northeast), and Susu in Maritime Guinea (southwest).
However, as the map below shows, significant sections of the population of each region speak other languages. Ensuring effective two-way communication therefore entails provision for both listening and information relay in the minority as well as the majority languages for the area. Urban areas are especially linguistically diverse. On average 14 languages are spoken in urban areas, compared with eight languages on average in rural areas.
Sixty-five percent of the Guinean population can’t read or write. Illiteracy is more present in urban areas (80%) than in rural areas (42%). Seventy-five percent of women and girls and 54% of men and boys above the age of 12 are not literate.
Thirty-one percent of Guineans can read and write in a foreign language: 54% of the urban population and 17% of rural residents.
Explore the data at the sub-prefecture level here.
These maps and datasets are published with funding from the World Food Programme.
Maps and resources:
Static map highlighting the most common languages spoken in Guinea. Data is from the 2014 census.
Static map highlighting the most common languages spoken in Guinea. Data is from the 2014 census.
Interactive map showing the number of speakers and geographic spread of different languages in Guinea. Data is from the 2014 census.
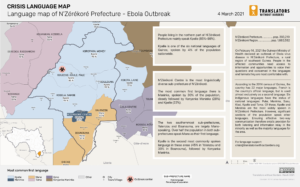
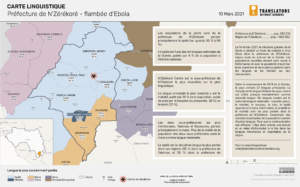
Languages spoken in N’Zérékoré prefecture in Guinea following the Ebola Outbreak – 5 March 2021.
Languages spoken in N’Zérékoré prefecture in Guinea following the Ebola Outbreak – 5 March 2021.